The Importance of Quality of Service (QoS) in VoIP
Share
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications are becoming increasingly common in businesses around the world due to their many benefits, including cost reduction and flexibility. However, in order to ensure consistently high call quality, it is critical to understand and properly implement the concept of Quality of Service (QoS).
What is Quality of Service (QoS)?
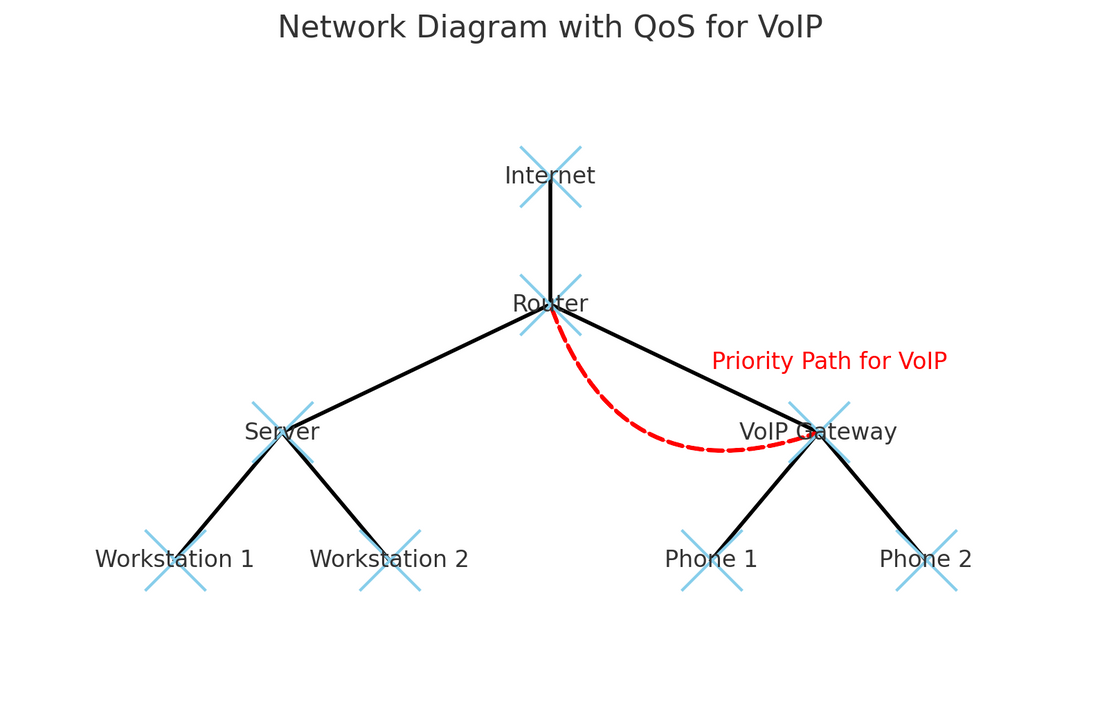
QoS is a set of technologies and practices that ensure the ability of a network to transmit data with a given level of performance. In the context of VoIP, QoS is essential to ensure that voice calls are clear, free of interruptions and delays. This is done by prioritizing voice data packets over other types of network traffic.
Why is QoS Crucial for VoIP?
- Reducing Latency (Latency):Latency is the delay that data takes to travel from one point to another. For a smooth voice conversation, latency should be as low as possible. QoS helps minimize this delay, making communication more natural.
- Jitter Elimination: Jitter is the variation of delay in packet arrival times. High jitter can cause interruptions and distortions in the call. QoS stabilizes the flow of packets, thus reducing jitter.
- Prevention of Packet Loss: Packet loss occurs when data does not reach its destination. In VoIP, this can result in missing words or degraded audio quality. QoS ensures that voice packets are transmitted reliably.
How to Implement QoS for VoIP
- Identifying VoIP Traffic: The first step is to identify VoIP traffic within the network. This can be done using protocols such as DiffServ (Differentiated Services) that mark VoIP packets.
- Traffic Prioritization: Once identified, VoIP packets must be prioritized against other types of traffic, such as email or file downloads. This ensures that voice calls receive a preferred lane in the network.
- Bandwidth Management: Allocating a portion of bandwidth exclusively for VoIP traffic can prevent congestion and ensure consistent call quality even during periods of high traffic.
- Configuring Routers and Switches: Configuring network devices to support QoS is essential. This includes setting priority queues and enabling features such as traffic shaping and traffic policing.
Tools and Technologies for QoS
- DiffServ (Differentiated Services): A packet marking protocol that assigns different priority levels to different types of traffic.
- MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching): A technology that routes traffic efficiently through the network, reducing latency and improving QoS.
- Traffic Shaping: Controls the amount and speed of traffic entering and leaving the network to prevent congestion.
- Traffic Policing: Limits traffic that exceeds a certain threshold, ensuring that the network is not overloaded.
